Monday, January 21, 2013
This article is an update of all the latest Memory module found in the latest Desktop and Servers, the last article was published in June 2007
288pin DDR4 DIMM Module
288 pin DDR4 Registered DIMMs are used to provide DDR4 SDRAM memory for the next generation of new servers and motherboards that use DDR4 technology. DDR4 is a leading-edge generation of memory with an improved architecture that allows it to transmit data very fast. .
Each 288-pin DDR4 DIMM provides a 64-bit data path (72-bit for ECC or registered modules).

DDR4 SDRAM will be packaged in a DIMM modules form factor.
256pin DDR4 SODIMM Module
256 pin DDR4 SODIMMs are used to provide DDR4 SDRAM memory for the next generation of new Laptop and Notebooks that use DDR4 technology. DDR4 is a leading-edge generation of memory with an improved architecture that allows it to transmit data very fast. .
Each 256-pin DDR4 SDIMM provides a 64-bit data path.

240pin DDR3 LRDIMM Module
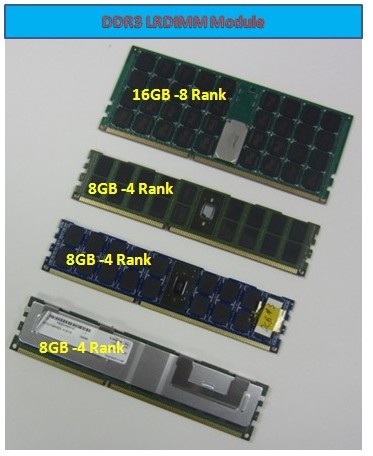
Load reduced DIMM (LRDIMM) is another new memory technology in development. Designed with a buffer chip (or chips) to replace the register to help minimize loading, the LRDIMM is targeted to increase overall server system memory capacity and speed using a memory buffer chip or chips as opposed to a register
240pin Unbuffered DDR3 DIMM

240-pin DDR2 Unbuffered DIMMs are used to provide DDR3 SDRAM memory for the next generation of new servers and motherboards that use DDR3 technology. DDR3 is a leading-edge generation of memory with an improved architecture that allows it to transmit data very fast. .
Each 240-pin DDR3 DIMM provides a 64-bit data path (72-bit for ECC or registered modules).
DDR3 SDRAM will be packaged in a DIMM modules form factor.
| DIMM Module |
Chip Type |
Clock Speed |
Data Rate |
Transfer Rate |
| PC3-6400 |
DDR3-800 |
400 |
800 |
6,400 |
| PC3-8500 |
DDR3-1066 |
533 |
1066 |
8,530 |
| PC3-10667 |
DDR3-1333 |
667 |
1333 |
10,660 |
| PC3-12800 |
DDR3-1600 |
800 |
1600 |
12,800 |
| PC3-14900 |
DDR3-1866 |
933 |
1866 |
14,930 |
DDR3 240-pin Unbuffered DIMMs are available in DDR3 PC3-6400 SDRAM and DDR3 PC3-7000 SDRAM. .
To use DDR3 Unbuffered DIMMs, a DDR3 server or motherboard must use DDR3 architecture. A DDR3 DIMM will not fit into a standard DDR2 , DDR2 FBDIMM and DDR socket.
The number of black components on a DDR3 240-pin DIMM varies and similar to DDR2 DIMM, but it always has 120 pins on the front and 120 pins on the back, for a total of 240. 240-pin DIMMs are approximately 5.25 inches long and 1.18 inches high, though the heights can vary.
The notch in a 240-pin DDR3 DIMM is in a different location than the notch for regular 240-pin DDR2 & FBDIMM modules.
240pin Fully Buffered DDR2 DIMM
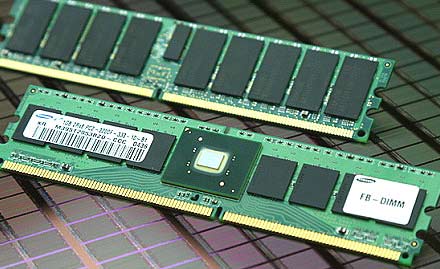
240-pin fully buffered DIMMs (FBDIMMs) are used to provide DDR2 SDRAM memory for servers and motherboards that use FBDIMM technology. DDR2 is a leading-edge generation of memory with an improved architecture that allows it to transmit data very fast. FBDIMM technology utilizes an advanced memory buffer that allows modules to be connected in series — meaning that more memory modules can be connected.
Each 240-pin DIMM provides a 64-bit data path (72-bit for ECC or registered or fully buffered modules).
DDR2 240-pin fully buffered DIMMs are available in DDR2 PC2-4200 SDRAM and DDR2 PC2-5300 SDRAM. .
To use fully buffered DIMMs, a FBDIMM server or motherboard must use FBDIMM architecture. An FBDIMM will not fit into a standard DDR2 socket, and a DDR2 module will not fit into an FBDIMM socket.
The number of black components on a 240-pin DIMM varies, but it always has 120 pins on the front and 120 pins on the back, for a total of 240. 240-pin DIMMs are approximately 5.25 inches long and 1.18 inches high, though the heights can vary.
The notch in a 240-pin fully buffered DDR2 DIMM is in a different location than the notch for regular 240-pin DDR2 modules
Standard 240-pin DDR2 DIMM

A dual inline memory module (DIMM) consists of a number of memory components (usually black) that are attached to a printed circuit board (usually green). The gold pins on the bottom of the DIMM provide a connection between the module and a socket on a larger printed circuit board. The pins on the front and back of a DIMM are not connected to each other.
240-pin DIMMs are used to provide DDR2 SDRAM memory for desktop computers. DDR2 is a leading-edge generation of memory with an improved architecture that allows it to transmit data very fast.
Each 240-pin DIMM provides a 64-bit data path (72-bit for ECC or registered modules).
Standard DDR2 240-pin DIMMs are available in DDR2 PC2-3200 SDRAM, DDR2 PC2-4200 SDRAM, and DDR2 PC2-5300 SDRAM.
To use DDR2 memory, your system motherboard must have 240-pin DIMM slots and a DDR2-enabled chipset. A DDR2 SDRAM DIMM will not fit into a standard SDRAM DIMM socket or a DDR DIMM socket.
The number of black components on a 240-pin DIMM can vary, but it always has 120 pins on the front and 120 pins on the back, for a total of 240. 240-pin DIMMs are approximately 5.25 inches long and 1.18 inches high, though the heights can vary. While 240-pin DDR2 DIMMs, 184-pin DDR DIMMs, and 168-pin DIMMs are approximately the same size, 240-pin DIMMs and 184-pin DIMMs have only one notch within the row of pins. The notch in a 240-pin DDR2 DIMM is closer toward the center of the module.
High Performance 240-pin DDR2 DIMM
What is High Performance DDR2 memory ?

High Performance memory is specifically built for performance enthusiasts who want to push the performance envelope while adding flash appeal to their boxes. High-performance memory modules features advanced speed grades, low latencies, and integrated aluminum heat spreaders. Some memory module features different colour PCB, and use black, blue,gold,silver colour...etc integrated heat spreaders, and even some have "chasing" red and green LEDs atop the module, circulating at varying speeds proportional to usage. A custom-designed circuit relays bus activity to the LEDs, allowing them to accurately reflect usage of each memory module.
A Dual inline memory module (DIMM) consists of a number of memory components that are attached to a black printed circuit board. The gold pins on the bottom of the DIMM provide a connection between the module and a socket on a larger printed circuit board. The pins on the front and back of a DIMM are not connected to each other.
High performance 240pin DIMMs are used to provide DDR2 SDRAM memory for desktop computers. DDR2 is a leading-edge generation of memory with an improved architecture that allows it to transmit data very fast. This 240-pin DIMMs are available in DDR2 PC2-5300 (DDR2 667) SDRAM.
To use DDR2 memory, your system motherboard must have 240-pin DIMM slots and a DDR2-enabled chipset. A DDR2 SDRAM DIMM will not fit into a standard SDRAM DIMM socket or a DDR DIMM socket.
The number of black components on a high performing 240-pin DIMM can vary, but it always has 120 pins on the front and 120 pins on the back, for a total of 240. The 240-pin DIMMs are approximately 5.25 inches long and 1.18 inches high, though the heights can vary. While 240-pin DDR2 DIMMs, 184-pin DDR DIMMs, and 168-pin DIMMs are approximately the same size, 240-pin DIMMs and 184-pin DIMMs have only one notch within the row of pins. The notch in a 240-pin DDR2 DIMM is closer toward the center of the module.
Standard 184-pin DDR DIMM

Approximately 5.25 in. by 1.25 in. (133.35 mm by 31.75 mm)
A dual inline memory module (DIMM) consists of a number of memory components (usually black) that are attached to a printed circuit board (usually green). The gold pins on the bottom of the DIMM provide a connection between the module and a socket on a larger printed circuit board. The pins on the front and back of a DIMM are not connected to each other.
184-pin DIMMs are used to provide DDR SDRAM memory for desktop computers. Standard 184-pin DIMMs are available in PC1600 DDR SDRAM, PC2100 DDR SDRAM, PC2700 DDR SDRAM, and PC3200 SDRAM.
To use DDR memory, your system motherboard must have 184-pin DIMM slots and a DDR-enabled chipset. A DDR SDRAM DIMM will not fit into a standard SDRAM DIMM socket.
The number of black components on a 184-pin DIMM can vary, but it always has 92 pins on the front and 92 pins on the back, for a total of 184. 184-pin DIMMs are approximately 5.25 inches long and 1.25 inches high, though the heights can vary. While 184-pin DIMMs and 168-pin DIMMs are approximately the same size, 184-pin DIMMs have only one notch within the row of pins.
High Performance 184-pin DDR DIMM

What is High Performance DDR memory ?
This type of memory is specifically built for performance enthusiasts who want to push the performance envelope without worrying about data loss or corruption, mysterious intermittent errors and display problems, or worse — the dreaded BSOD! The high-performance memory modules features advanced speed grades, low latencies, and integrated aluminum heat spreaders.
A dual inline memory module (DIMM) consists of a number of memory components that are attached to a black printed circuit board. The gold pins on the bottom of the DIMM provide a connection between the module and a socket on a larger printed circuit board. The pins on the front and back of a DIMM are not connected to each other.
The 184-pin DIMMs are used to provide DDR1 SDRAM memory for desktop computers. High Performance 184-pin DIMMs are available in PC3200 DDR (DDR400) SDRAM and PC4000 DDR (DDR500) SDRAM.
To use DDR memory, your system motherboard must have 184-pin DIMM slots and a DDR-enabled chipset. A DDR SDRAM DIMM will not fit into a standard SDRAM DIMM socket.
The number of black components on a 184-pin DIMM can vary, but it always has 92 pins on the front and 92 pins on the back, for a total of 184. 184-pin DIMMs are approximately 5.25 inches long and 1.25 inches high, though the heights can vary. While 184-pin DIMMs and 168-pin DIMMs are approximately the same size, 184-pin DIMMs have only one notch within the row of pins
184 Pin RIMM

* The 184 pin RIMM are used in the latest Intel 820/840/850 Rambus PC System.
* The 184 pin RIMM module comes in both 16bit and 18bit ECC configuration and memory capacity range from 64 to 512 megabyte.
* The rambus memory chip is package in a Ball Grid Array (BGA) form factor.
* One of the key features of Rambus memory is its high operating frequency which comes in grades of 600,700 and 800Mhz.
* Power needed to drive the rambus chip is only 2.5 Volts
168-pin SDRAM DIMM

Approximately 5.25 in. by 1.375 in. (133.35 mm by 34.92 mm)
A dual inline memory module (DIMM) consists of a number of memory components (usually black) that are attached to a printed circuit board (usually green). The gold pins on the bottom of the DIMM provide a connection between the module and a socket on a larger printed circuit board. The pins on the front and back of a DIMM are not connected.
168-pin DIMMs are commonly found in Pentium® and Athlon® systems. 168-pin DIMMs are available in EDO, 66MHz SDRAM, PC100 SDRAM, and PC133 SDRAM. When upgrading, be sure to match the memory technology that is already in your system.
The number of black components on a 168-pin DIMM can vary, but it always has 84 pins on the front and 84 pins on the back, for a total of 168. 168-pin DIMMs are approximately 5.25 inches long and 1.375 inches high, though the heights can vary. They have two small notches within the row of pins along the bottom of the module
144 MicroDIMM

Approximately 1.545 in. by 1 in. (39.2 mm by 25.4 mm)
144pin SDRAM Micro-DIMM
A micro dual inline memory module (MicroDIMM) consists of a number of memory components (usually black) that are attached to a printed circuit board (usually green). MicroDIMMs get their name because they are smaller than both regular DIMMs and SODIMMs. The gold pins on the bottom of the MicroDIMM provide a connection between the module and a socket on a larger printed circuit board. The pins on the front and back of a MicroDIMM are not connected, providing two lines of communication paths between the module and the system.
144-pin MicroDIMMs are commonly found in sub-notebook computers. 144-pin MicroDIMMs are available in PC133 SDRAM. When upgrading, be sure to match the memory technology that is already in your system.
The number of black components on a 144-pin MicroDIMM can vary, but they always have 72 pins on the front and 72 pins on the back for a total of 144. 144-pin MicroDIMMs are approximately 1.545 inches long and 1 inch high, though the heights can vary. Unlike SODIMMs, MicroDIMMs do not have any notches along the bottom edge
172 DDR MicroDIMM

The number of black components on a 172-pin MicroDIMM can vary, but they always have 86 pins on the front and 86 pins on the back for a total of 172. 172-pin MicroDIMMs are approximately 1.67 inches long and 1.18 inch high, though the heights can vary. Unlike SODIMMs, MicroDIMMs do not have any notches along the bottom edge
214pin DDR2 MicroDIMM

The number of black components on a 214-pin MicroDIMM can vary.. 214-pin MicroDIMMs are approximately 54 mm long and 30mm high, though the heights can vary. Unlike SODIMMs, MicroDIMMs do not have any notches along the bottom edge and uses a new 2 piece type of connector known as the " Mezzanine Socket.
100-pin DIMM

Approximately 3.5 in. by 1.25 in. (88.9 mm by 31.75 mm)
A dual inline memory module (DIMM) consists of a number of memory components (usually black) that are attached to a printed circuit board (usually green). The gold pins on the bottom of the DIMM provide a connection between the module and a socket on a larger printed circuit board. The pins on the front and back of a DIMM are not connected.
100-pin DIMMs are commonly found in printers. The number of black components on a 100-pin DIMM can vary, but it always has 50 pins on the front and 50 pins on the back, for a total of 100. 100-pin DIMMs are approximately 3.5 inches long and 1.25 inches high, though the heights can vary. They have two small notches within the row of pins along the bottom of the module.
DDR 200-pin SODIMM

Approximately 2.625 in. by 1.25 in. (66.7 mm by 31.75 mm)
DDR2 200-pin SODIMM

Approximately 2.625 in. by 1.25 in. (66.7 mm by 31.75 mm)
A small outline dual inline memory module (SODIMM) consists of a number of memory components (usually black) that are attached to a printed circuit board (usually green). SODIMMs get their name because they are smaller and thinner than regular DIMMs. The gold pins on the bottom of the SODIMM provide a connection between the module and a socket on a larger printed circuit board. The pins on the front and back of a SODIMM are not connected.
200-pin SODIMMs are used to provide DDR SDRAM memory for notebook computers. 200-pin SODIMMs are available in PC2100 DDR SDRAM, PC2700 DDR SDRAM, and PC3200 DDR SDRAM. To use DDR memory, your system motherboard must have 200-pin SODIMM slots and a DDR-enabled chipset. A DDR SODIMM will not fit into a standard SDRAM SODIMM socket.
The number of black components on a 200-pin SODIMM can vary, but it always has 100 pins on the front and 100 pins on the back, for a total of 200. 200-pin SODIMMs are approximately 2.625 inches long and 1.25 inches high, though the heights can vary. Like 144-pin SODIMMs, 200-pin SODIMMs have one small notch within the row of pins; however, the notch on the 200-pin SODIMMs is closer to the left side of the module.
144-pin SODIMM

Approximately 2.625 in. by 1.25 in. (66.7 mm by 31.75 mm)
A small outline dual inline memory module (SODIMM) consists of a number of memory components (usually black) that are attached to a printed circuit board (usually green). SODIMMs get their name because they are smaller and thinner than regular DIMMs. The gold pins on the bottom of the SODIMM provide a connection between the module and a socket on a larger printed circuit board. The pins on the front and back of a SODIMM are not connected.
144-pin SODIMMs are commonly found in notebook computers. 144-pin SODIMMs are available in EDO, 66MHz SDRAM, PC100 SDRAM, and PC133 SDRAM. When upgrading, be sure to match the memory technology that is already in your system.
The number of black components on a 144-pin SODIMM can vary, but it always has 72 pins on the front and 72 pins on the back, for a total of 144. 144-pin SODIMMs are approximately 2.625 inches long and 1.25 inches high, though the heights can vary. They have one small notch within the row of pins along the bottom of the module.
72-pin SIMM

Approximately 4.25 in. by 1 in. (108 mm by 25.4 mm)
A single inline memory module (SIMM) consists of a number of memory components (usually black) that are attached to a printed circuit board (usually green). The gold or tin pins on the bottom of the SIMM provide a connection between the module and a socket on a larger printed circuit board. The pins on the front and back of a SIMM are connected.
72-pin SIMMs are commonly found in older desktop computers, such as the 486 and early Pentium® models. 72-pin SIMMs are available in FPM or EDO. When upgrading, be sure to match the memory technology that is already in your system.
The number of black components on a 72-pin SIMM can vary. 72-pin SIMMs are approximately 4.25 inches long and 1 inch high, though the heights can vary. They have one notch on the bottom left and one notch in the center of the module
30 Pin SIMMs

* The 30 Pin SIMMs was the 1st generation SIMM memory which are typically found in older Intel 286 and 386 desktop computer system.
* The 30pin SIMM module comes in both 8 bit and 9 bit(parity) configuration and memory capacity range from 256K to 8 megabyte.
* 30pin SIMM comes in only 5 Volts and speed range from 60ns to 80ns.
* The DRAM types supported are mostly Page Mode and Nibble Mode DRAM which comes in both DIP, PLCC and SOJ package
By: DocMemory
Copyright © 2013 CST, Inc. All Rights Reserved
|


